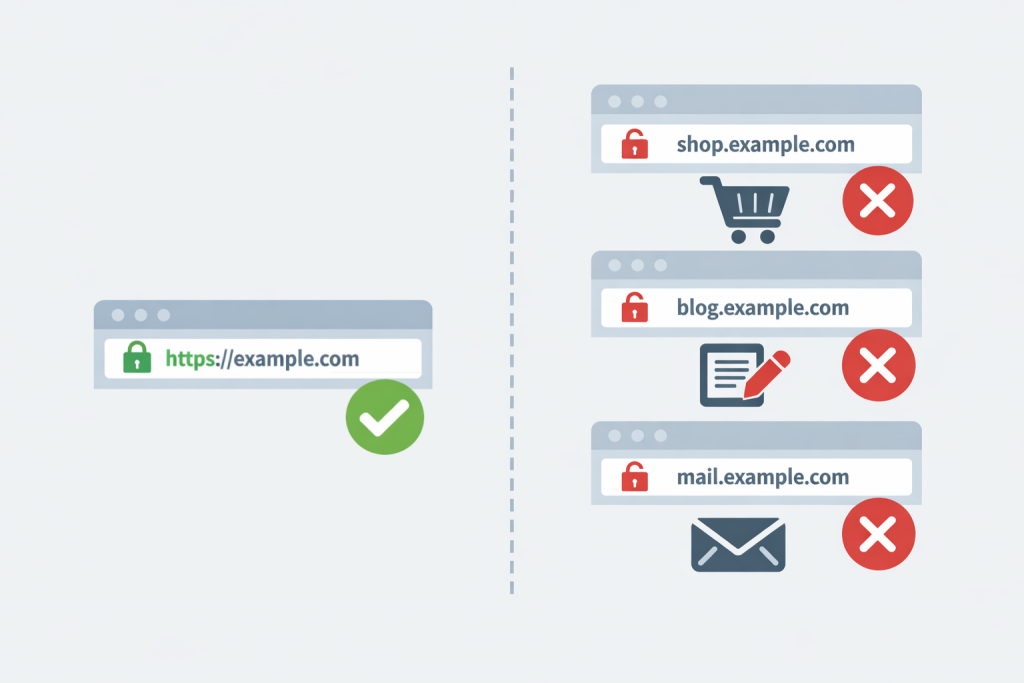
Many website owners face a situation where an SSL certificate works successfully for the main domain, but the browser shows a security warning when accessing a subdomain. For example, the site opens correctly at example.com, but when trying to visit blog.example.com or mail.example.com, a message about an invalid certificate appears. For users, this looks like an error or a technical failure, but in reality, this behavior has clear and logical reasons related to the type of SSL certificate and how it works.









